
Today I added images to a outline of a Maori hoe

Today I added images to a outline of a Maori hoe
Polynesian Explorers
Highlight the correct answer, or type in what you think is correct.
Did this prophecy come true? Explain.
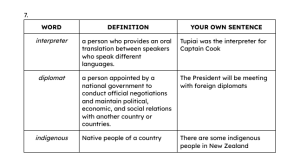
→Yes it’s said in the book On 18 June 1767, a strange vessel was
seen off the coast of Tahiti, where Tupaia now lived.
→He was the translator for Captain Cook
7.
8. Explain the four reasons why Hoe were important, and special pieces of technology for Maori.
→ they were important to the Maori culture.
→ They had spiritual importance.
→ They were important in all areas of life.
→ They were extremely well designed.
9. Tupaia (up until recently) and much more Polynesian history remains oral history (that means told by speaking). How can we ensure that this history is available to learn for future generations? Try to come up with at least 2 ways.
→ we can learn from stories in books and not forget our history.
Today I learnt about the different ways to learn about information in a graph
Treaty of Waitangi
Highlight the correct answer, or type in what you think is correct.
1. When did Maori first arrive in Aotearoa, New Zealand?
a) Between 1150 & 1200AD
b) Between 1250 & 1350AD
c) Between 1250 & 1300AD
d) Last Year
2. In the 1790’s Pakeha arrived in NZ to do what?
a) Hunt Moa b) Start families
c) Hunt whale & seals d) Escape prison sentences
3. What was the name of the British official sent to secure British rule over NZ?
a) William Johnson b) Abel Tasman
c) William Hobson d) Captain James Cook
4. There were two things that Maori chiefs Hone Heke Pokai and Tamati Waka Nene thought signing the treaty would help accomplish. What were they?
→They wanted control on sales of Māori land to Europeans and on European settlers
→Māori possessions under the crown’s protection, with the exclusive right of the queen to purchase Māori land
5. True or False: Te Tiriti o Waitangi and the Treaty of Waitangi are the exact same.
a) True b) False
6. The Waitangi Tribunal was set up in 1975. Describe the job the Waitangi Tribunal have?
→Makes recommendations on claims brought by Māori relating to Crown actions which breach the promises made in the Treaty of Waitangi.
7.
WORD
DEFINITION
YOUR OWN SENTENCE
colonisation
The spreading of a species into a new habitat.
The British did a colonisation on NZ
treaty
The formal document embodying such an international agreement.
The Treaty of Waitangi
sovereignty
the quality or state of being sovereign, or of having supreme power or authority.
the quality or state of being sovereign
8. When the treaty was signed William Hobson said out loud “He iwi
tahi tātou.” (“We are one people.”)
What do you think he meant by this?
→we are all together and one
9. The article describes differences between Te Tiriti and the Treaty of Waitangi – Why do you think those differences caused difficulties?
→ because some stuff could be mixed up and get confused
Today we were thought about the Treaty of Waitangi it was a lot of fun.